Enabling the Badger
The Badger is a small application responsible for generating SVG badges representing either the current coverage percentage of a given repository, or the amount of issues checks found in the last run.
Enabling the Badger will allow users to visit a repository “Badges” page and copy a public URL to the badge image, and place them in the project’s README file or other accompanying documentation:
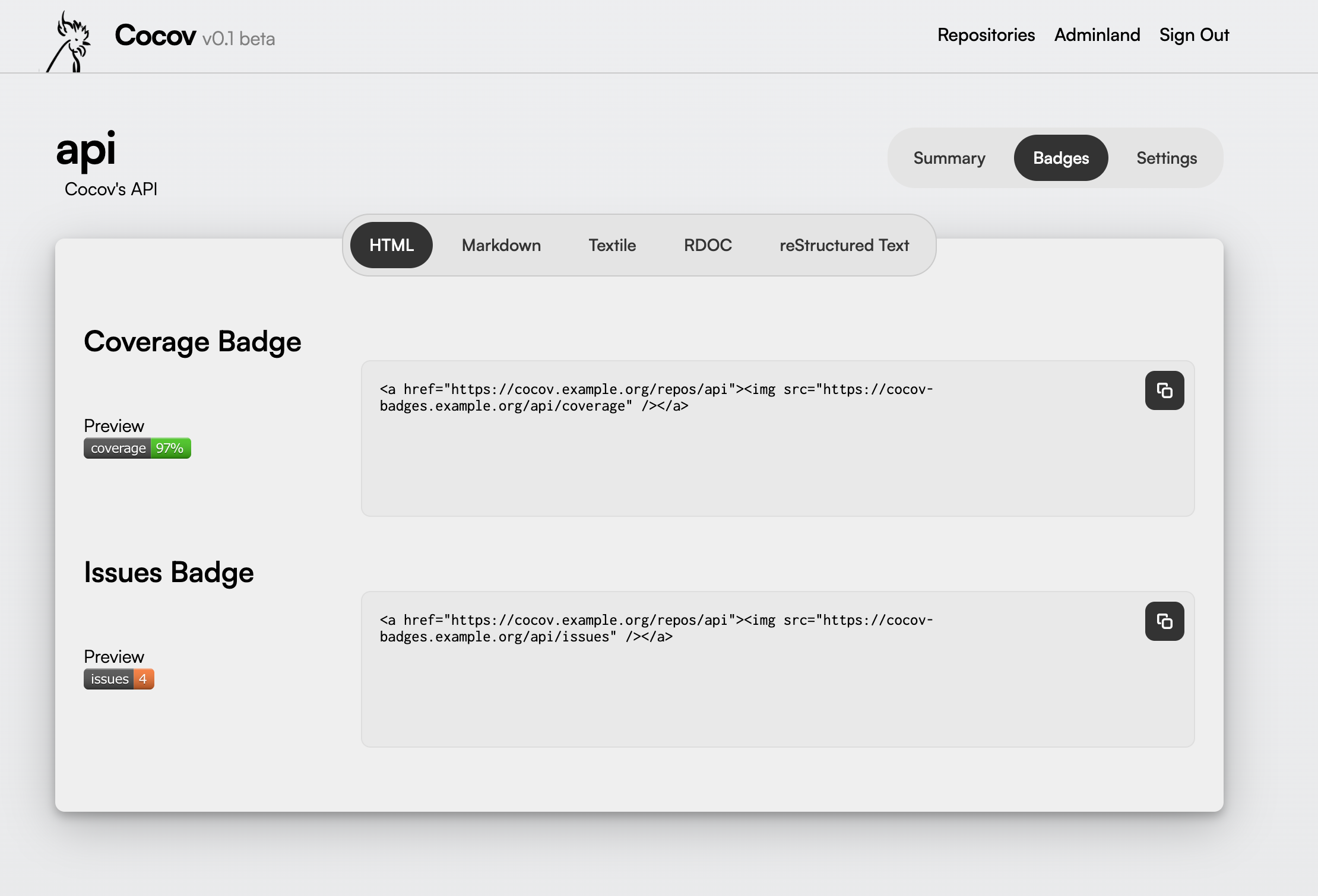
Requirements #
As stated in the Requirements page, Badger must be exposed to the public internet. This is due to how GitHub proxies all images present in READMEs, Wikis, Issues, and so on.
Configuring the Chart #
Just like Worker, Badger will need a Service Token to be able to communicate with the instance’s API. Access the Adminland, select Service Tokens, and create a new one, using a descriptive name. Take note of the token, since it will not be displayed again.
Notice: Initializing the Worker instance goes through the process of creating a Service Token in detail. Feel free to follow instructions from that section, if required.
The first step is to add a new badger section to your cocov configuration
section, and enable it through the enabled field:
1
2
3
cocov:
badger:
enabled: true
Then, provide the API Service Token you obtained in the previous step.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
cocov:
badger:
enabled: true
apiToken:
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: cocov-secrets
key: badger-api-token
Finally, configure the ingress to allow external connectivity. Like the API, the chart provides a simple ingress configuration to be used out of the box, but it is up to you to leverage it or not. In case you wish to, the following section describes how.
Using the Pre-Configured Ingress #
Badger provides its own pre-configured ingress, where only a ingressClassName,
hosts and potentially annotations need to be provided to it. The following
keys are accepted:
badger.ingress.enabled #
Whether the ingress is enabled or not. Disabling it prevents the ingress from being applied by the chart.
badger.ingress.annotations #
A set of annotations to be provided to the ingress
badger.ingress.hosts #
A list of hosts to be provided to the ingress
badger.ingress.tls #
A list of TLS configuration to be provided to the ingress
badger.ingress.ingressClassName #
ingressClassName is the name of an IngressClass cluster resource.
Ingress controller implementations use this field to know whether they should be
serving this Ingress resource, by a transitive connection (controller ->
IngressClass -> Ingress resource).
For instance, the following would enable the builtin ingress for badger:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
cocov:
badger:
# Required options would go here...
ingress:
enabled: true
ingressClassName: "nginx"
hosts:
- "cocov-badges.mydomain.com"
Finishing Up #
Apply chart changes, and monitor the badger startup process. During its preflight checks, it will attempt to check connectivity with the API. Do notice that this does not indicate that it is indeed healthy and the Service Token was correctly configured. To ensure this, check a repository’s “Badges” page to ensure that it is being displayed correctly.